| g e n u i n e i d e a s | ||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| home | art and science |
writings | biography | food | inventions | search |
| hitting the sweet spot | ||||||||||
|
Sept. 2013
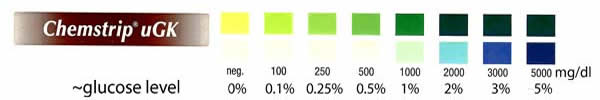
But what about sugar? Why do so many brines and rubs contain sugar? Is it worth the effort to float a Thanksgiving turkey in an apple cider and kosher salt bath for three days? Or is the inclusion of apple cider a mere affectation of the Fall season? A bit of kitchen science will help separate tradition from technique. Sugar molecules are MUCH larger than salt ions- over 10 times larger in cross-section and mass. It takes salt almost 24 hours to penetrate meat by an inch. So you might expect that a huge, lumbering sugar molecule would take its own sweet time. And you would be right. To validate this intuition, I immersed a pork tenderloin in a brine of pure white grape juice. Tenderloin is a uniform, pale and mostly fat free cut of meat- ideal for this kind of experiment. And white grape juice is sweet (15% sugar) and almost colorless. Plus, it has the advantage that commercially available urine test strips will detect the sugars in grape juice1. For example, the colors on these double-pad Chemstrips run from yellow to green, and white to blue, as the sugar level climbs from 0% to 5% (the bottom pad is more sensitive at high concentrations, the top pad at lower concentrations). We can assemble these pads into a ladder, so they will spatially record sugar concentration in the tenderloin.
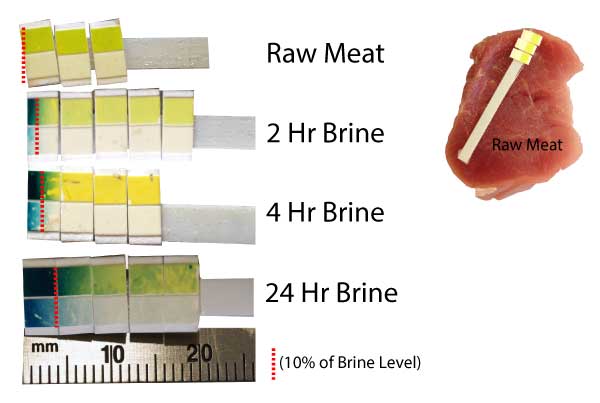
The test procedure is as follows, and is similar to our test protocol for salt diffusion:
Here are the results. I drew a dotted red line on the image at the 10% of initial brine (e.g. 1% absolute sugar) concentration level, indicating that 90% of the diffused sugar lays between the surface and this line.
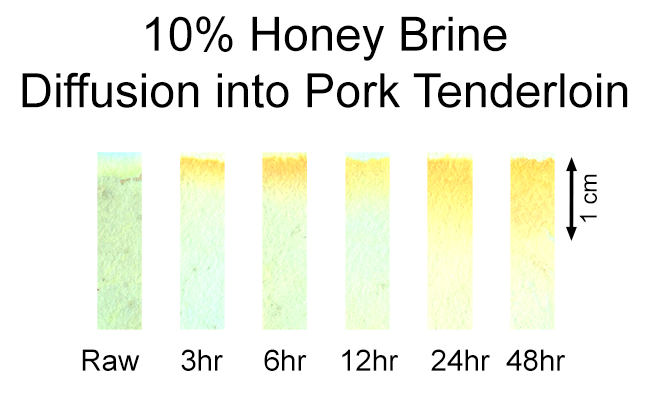
So sugar is barely absorbed by meat, even after a full day's brining. The diffusion rate is at least 5-10 times slower than salt1, . We also performed a second series of tests using Benedict's Reagent. Like the urine test, Benedict's only reacts with glucose or fructose, so we brined the pork tenderloin in a 10% honey bath (honey is around 50% glucose, 50% fructose). As with our salt diffusion experiments, the method was as follows:
Here are the results. Note the first few mms of pork also begin to sog out after a day or two (e.g. the muscle breaks down, some osmotic cell losses in parallel to sugar diffusing inward, etc). This spongy layer holds onto the brine, and if I hadn't patted off the surface, would turn bright yellow in this test:
While some sugar molecules do penetrate beyond a cm after two days in the brine, the test is more sensitive than your tongue and detects levels that simply do not taste sweet. By tasting 2mm thick slices of the meat sampled from the surface inward (cooking each slice before consuming, of course), only the first slice was sweet. And in this slice, the sugar supressed or masked the meat's "porkiness". So, even after a day of brining, sugar flavor only penetrates a few mms. Which again raises the question, why bother brining? If you enjoy eating sweetened meat, like ribs or pulled pork, it's likely they'll be glazed in a thick, sugary sauce before serving. A mm or so of slightly sweet, brined pork bark will go unnoticed beneath this onslaught of herbs, spices and brown sugar. Except for browning. Thanks to the "Maillard reaction", browned food looks good, tastes great and smells amazing. This essential reaction occurs between proteins and sugars, and ONLY when both are present. Unlike carmelization2 which only occurs above 230F, the Maillard reaction occurs even at room temperature. In fact, the reaction is percolating along inside your sweet, muscular body while you are patiently reading this article. Fortunately, like most chemical reactions, the Maillard sequence proceeds faster at higher temperatures. So you don't end up smelling like a hot-crossed bun. To test if a sugar brine enhances the Maillard reaction, I soaked a tenderloin in white grape juice for twenty four hours, rinsed the surface thoroughly, and then sliced off one end. The tenderloin was baked in a 375F oven until the interior reached 155F. As you can plainly tell, the sugar-brined surface is much darker than the freshly cut end. And its flavor profile was more complex and nuanced:
Brining will definitely accelerate browning, no matter what sugar you choose to use. Heat and sugar speeds up the Maillard reaction to the point where browning is significant after only 30 minutes in a 375F oven. Without absorbed sugar working in tandem with muscle protein, you would have to overcook the pork by hours to provide enough time for browning to occur merely from the small levels of naturally occurring sugar. So when you cook meat, add sugar to a brine if:
But don't bother with a sugar brine if you plan on cooking under a dark, sweet glaze or rub.
|
||||||||||
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 Chemstrips detect glucose in urine (a warning sign of diabetes) via an enzymatic reaction. They will not detect white table sugar, e.g. sucrose, which is "non-reducing". For this reason I used grape juice in the brine- chemically, it's about 50% fructose and 50% glucose. Sucrose is actually one fructose molecule bonded to one glucose molecule, and thus nearly twice as large and ungainly. A brine made with sucrose will diffuse even more slowly than glucose into meat. In your stomach, most sugars, including sucrose, high fructose corn syrup, honey and agave, are severed by hydrochloric acid into simple glucose and fructose. These smaller, simpler molecules are easier for the intestines to absorb. In principle, you can detect sucrose in meat by first treating the surface with an acid to hydrolyze (sever) the bonds, freeing glucose, then neutralizing the acid, and then exposing to the test strips. But this is a bit complex for the average kitchen scientist to safely and correctly implement. Results on vegetables are similar to meat, if a bit slower. Which explains why sweet pickles take weeks to fully develop their flavor, or why quick-pickles are sliced thin and often added to hot brines. Note the vegetable's skin was removed prior to brining:
2 Caramelization is the controlled burning of sugar. Unlike the Maillard Reaction, no proteins, enzymes or alkaline conditions are necessary, but heat is critical. If you place a slice of white bread in a 225F oven next to a bowl of table sugar and grape juice, and wait half a day, the bread will brown due to the Maillard Reaction (bread contains sugar and gluten proteins), the fructose in the grape juice caramelizes, and the sucrose in sugar remains snowy white. So a table sugar rub or glaze on a pork shoulder, indirectly heated in a 225F oven, never caramelizes. It will contribute to the Maillard reaction within the meat, but will not brown the glaze itself.
The required temperatures are:
Confusingly, the sticky candy known as "caramel" is brown and flavorful as a result of either the Maillard or caramelization reactions. Some recipes recommend cooking sugar and water until it turns brown around 350F. At this point, the hot caramelized sugar is removed from the heat and butter and cream is folded in, resulting in a smooth, sticky confection. But other recipes suggest simultaneously cooking a mixture of sugar, water and milk proteins until it reaches 250F- this is primarily a Maillard reaction-based "caramel". To my taste, the 350F caramelization reaction yields a more complex and pleasantly acrid flavor. The 250F Maillard caramel is insipid. If you plan on grilling meat with a sugar glaze, or bake above 230F, caramelization can occur on the outer-most, driest surfaces. Choose a fruit sugar glaze if your meat is nearly fully cooked, and you want the glaze to darken quickly without overcooking your dinner. Choose a sucrose (or maltose if available) glaze if you plan on grilling raw meat- the higher caramelization temperatures will protect against premature burning. 3 In principle, the Maillard reaction only occurs between amino acids (e.g. proteins like meat or wheat gluten) and reducing sugars, like fructose and glucose, but not sucrose (table sugar). However, sucrose will disintigrate into fructose and glucose with heat and a bit of acid. Many glazes contain acids, as do many foods. So almost any sugar will kick off the Maillard reaction, but the fruit sugars are more effective.
|
||||||||||
 Contact Greg Blonder by email here - Modified Genuine Ideas, LLC. |